5 microphone mode
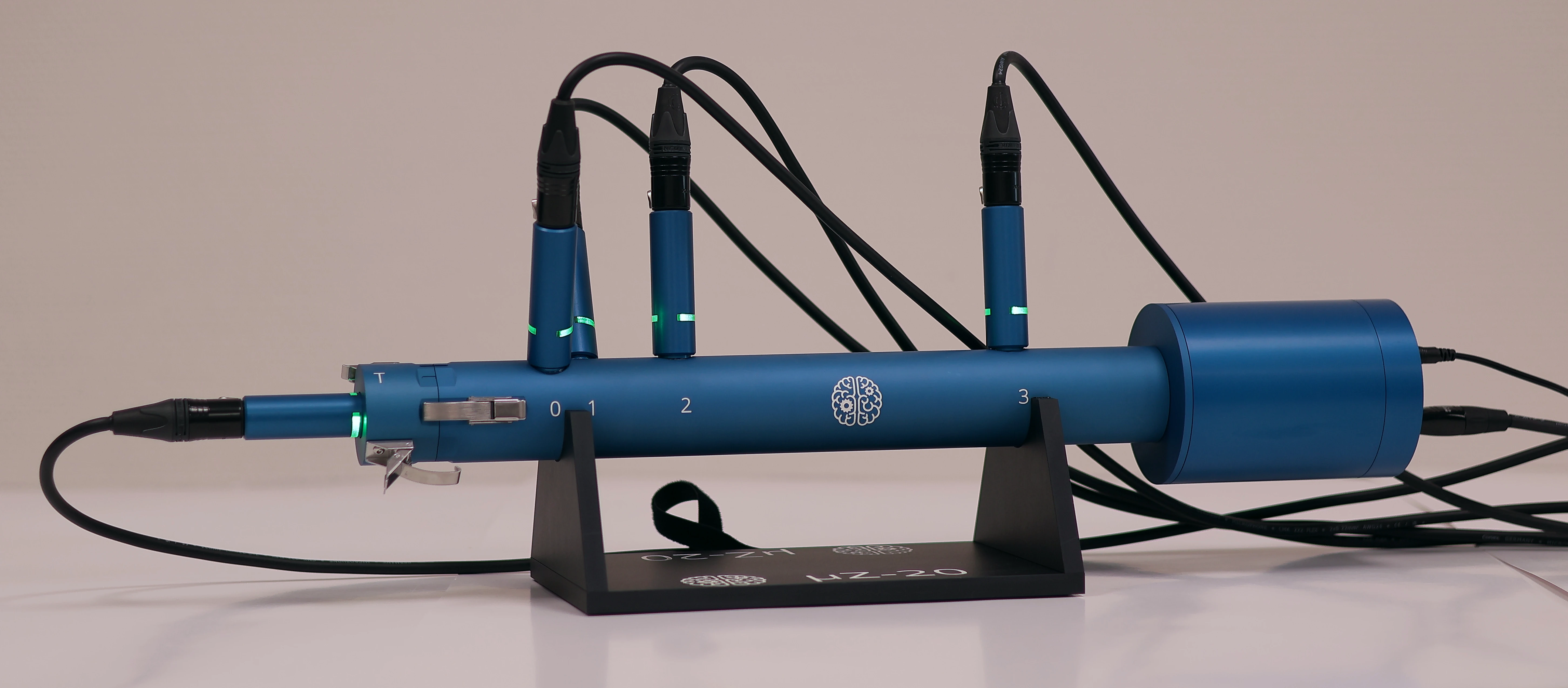

This configuration can be used to measure samples with impedances that are too high for the 4 microphone method. Since the volume velocity through these samples can't be determined by plane wave decomposition, it must be measured in a more direct way.
This is done using a 5th microphone, which is mounted in a cavity behind the sample. This microphone is referred to as the tip microphone. The pressure measured in the back cavity by the tip microphone is used to determine the volume velocity through the sample, which in turn is used to calculate the sample's acoustic properties.
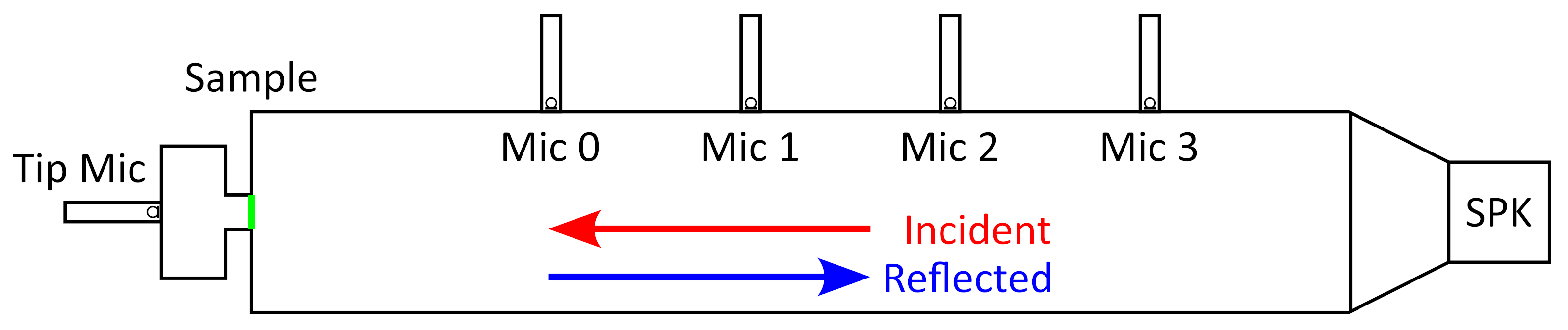
The reason why this method is not suitable for measurements on very low impedance samples, is that — at low frequencies — the impedance of the back cavity becomes large relative to the impedance of the sample. This results in numerical inaccuracies.
Back cavity size
The pressure levels measured at the tip microphone are affected by the size of the back cavity. The ideal cavity size depends on the properties of the samples under test. µZ comes with cavities in two sizes:
- 0.5 cc: This is the default cavity. It works well for most types of samples. For samples with very high impedance the pressure at the tip microphone can become insufficient at high frequencies.
- 0.1 cc: In this extra small cavity, a certain level of volume flow results in higher tip microphone pressures than in the 0.5 cc cavity. This yields better measurement results at high frequencies. However, the low-frequency impedance of this cavity is higher, which can limit performance in that frequency range.